General Information
Ruxolitinib Impurities and Ruxolitinib
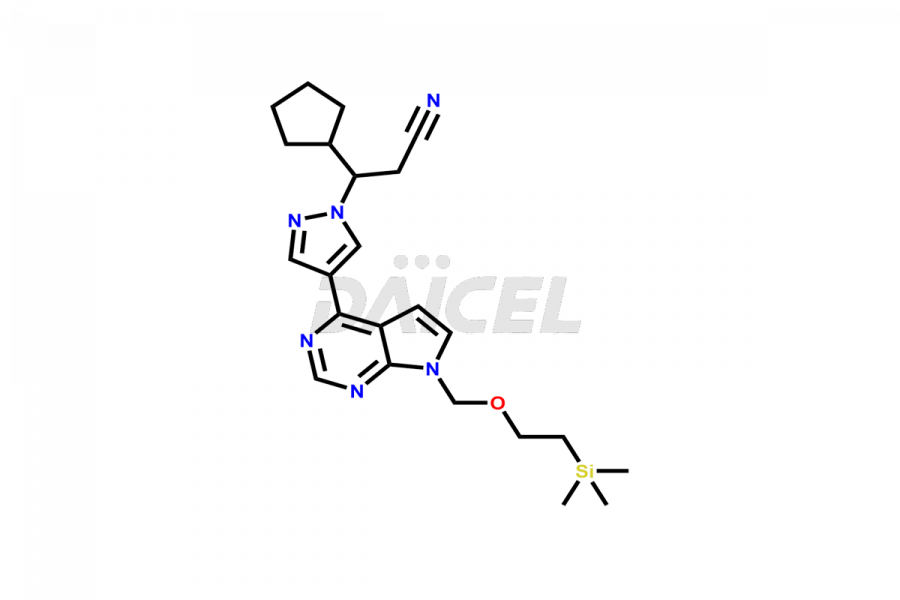
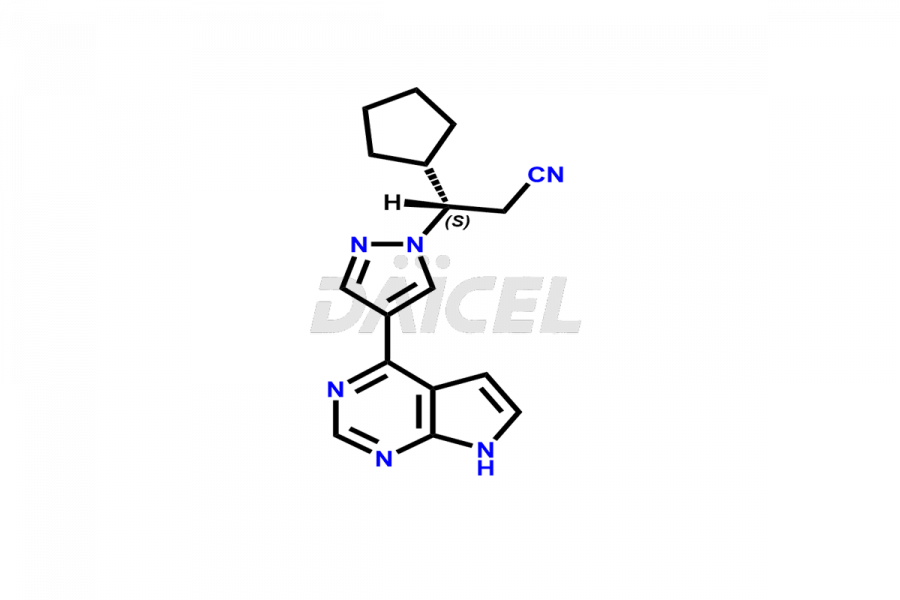
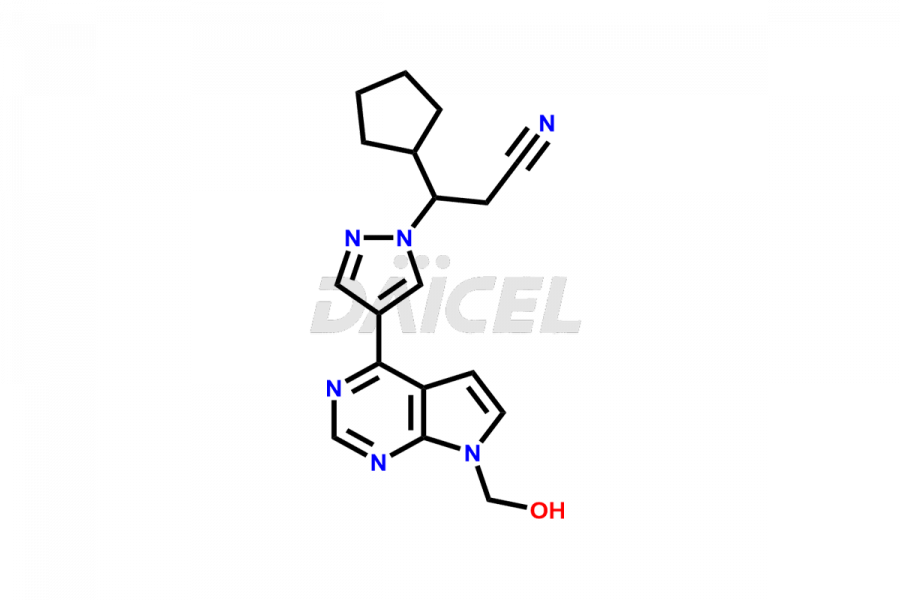
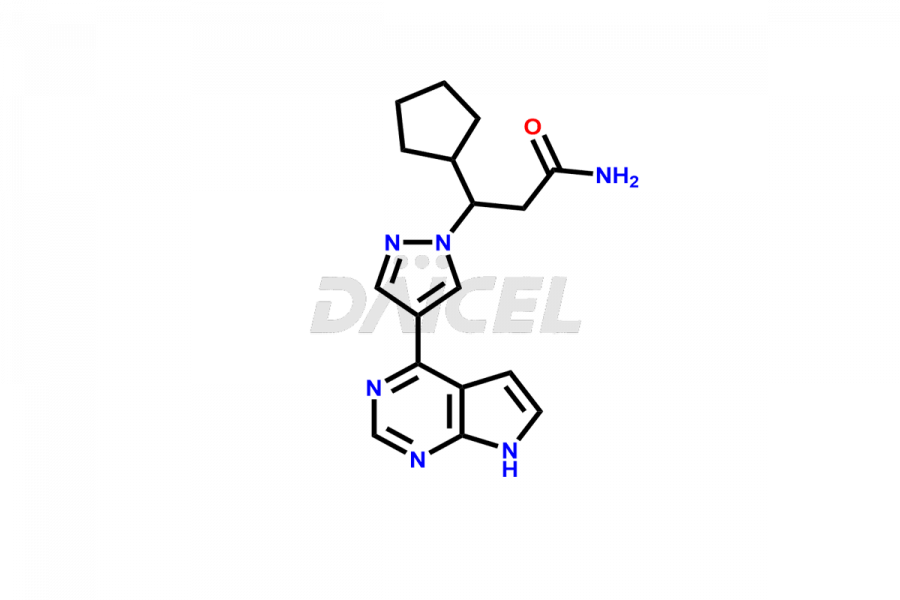
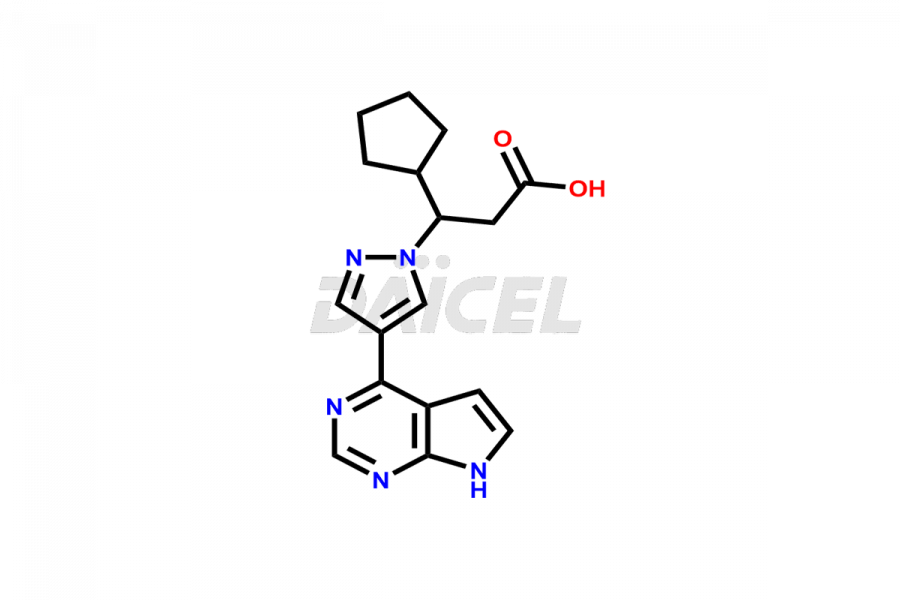
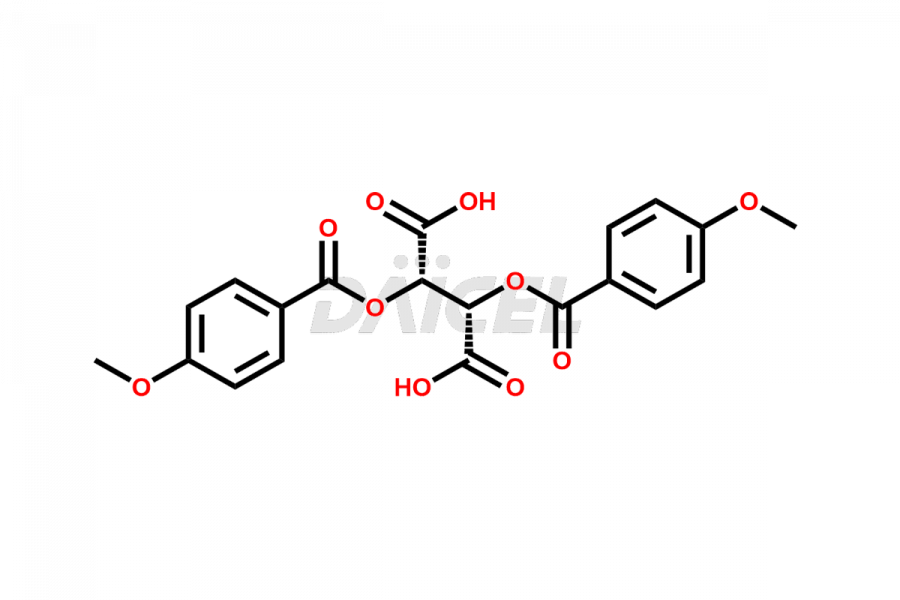
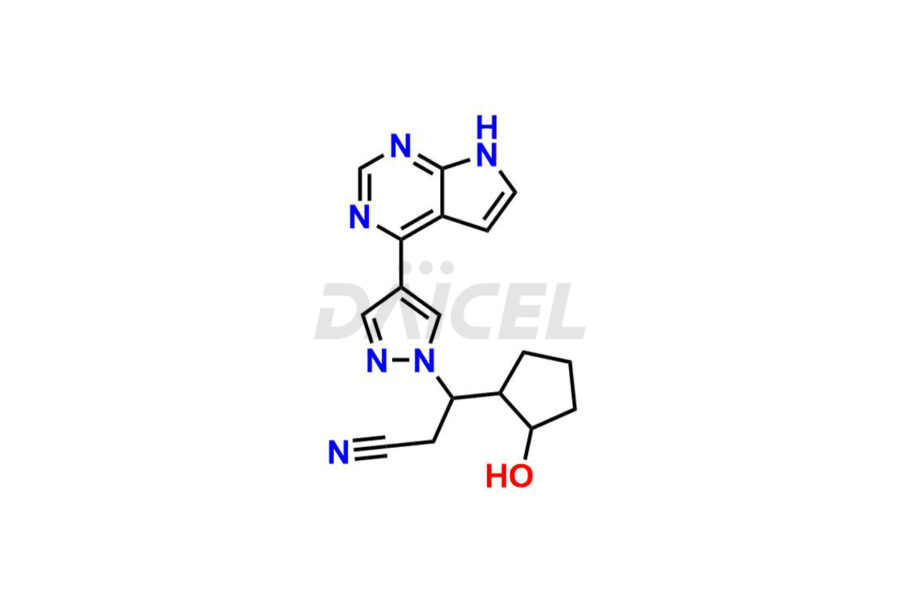
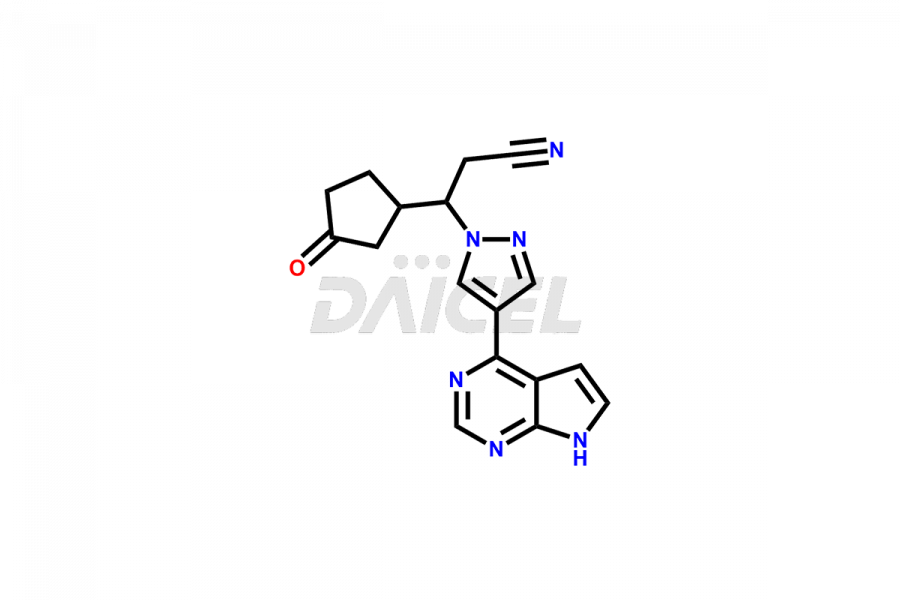
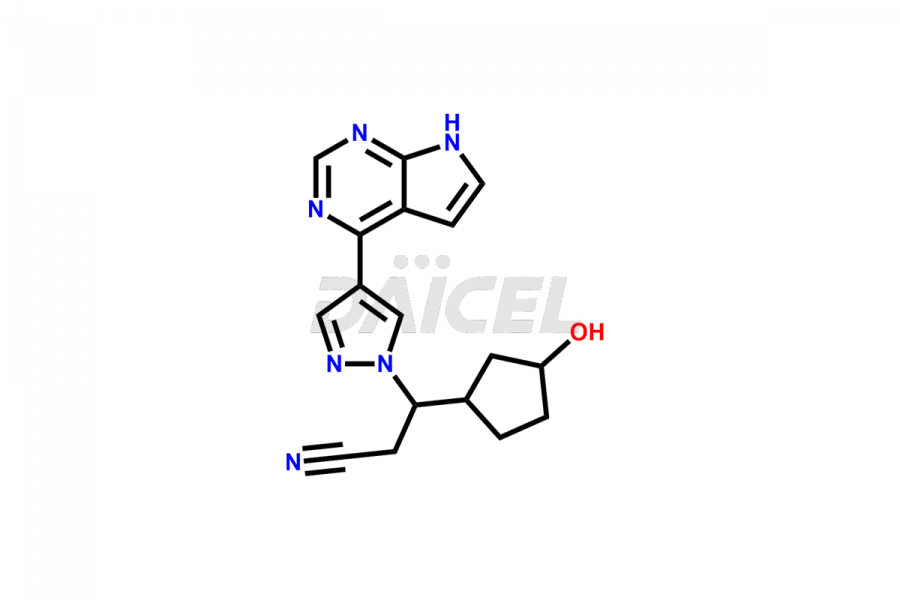
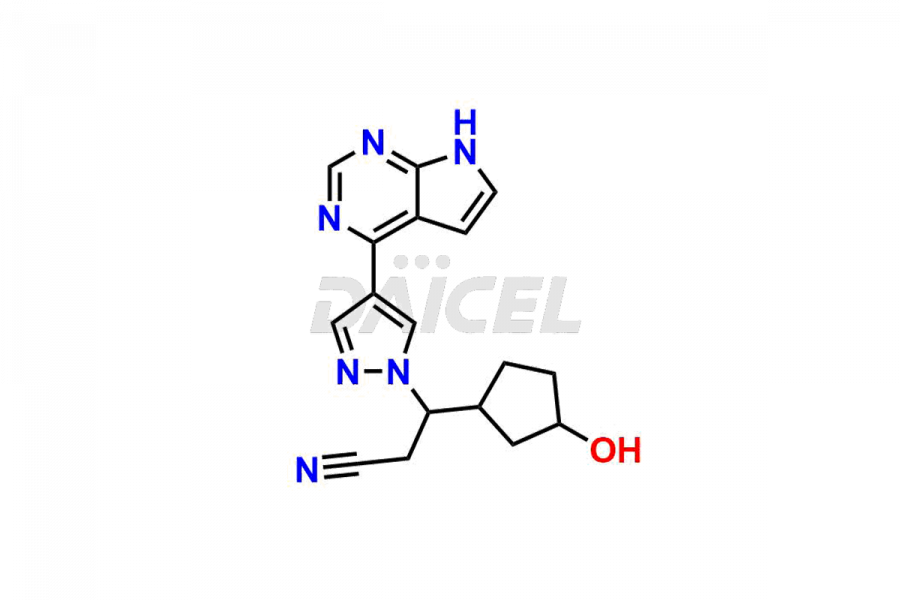
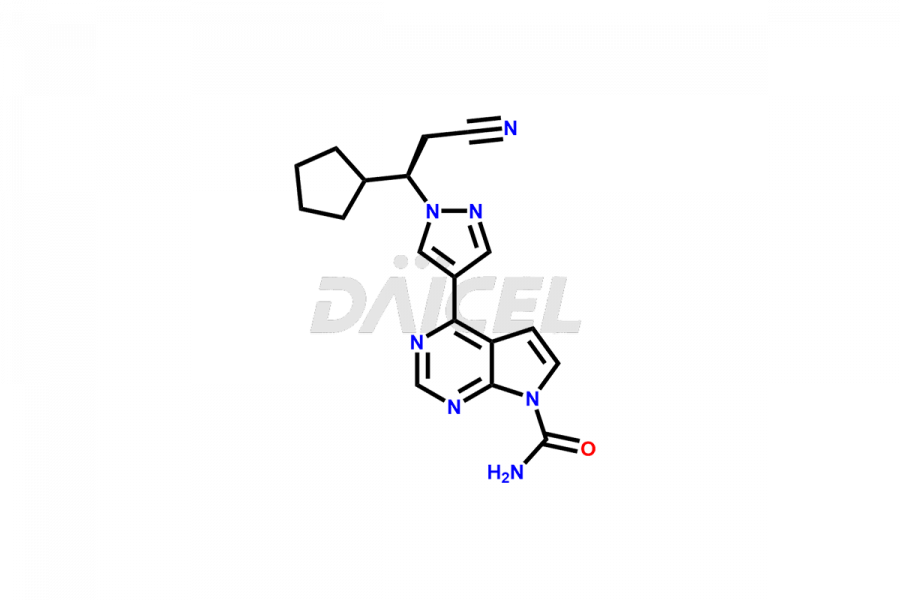
Daicel Pharma synthesizes more than twelve high-quality Ruxolitinib impurities, such as Ruxolitinib R-isomer, Ruxolitinib M18 Metabolite, Ruxolitinib Triphenylphosphine oxide, Ruxolitinib Acrylopyrimidine impurity, and more. They are crucial in determining the quality, stability, and biological safety of the active pharmaceutical ingredient, Ruxolitinib. Moreover, Daicel Pharma offers custom synthesis of Ruxolitinib impurities and delivers them globally.
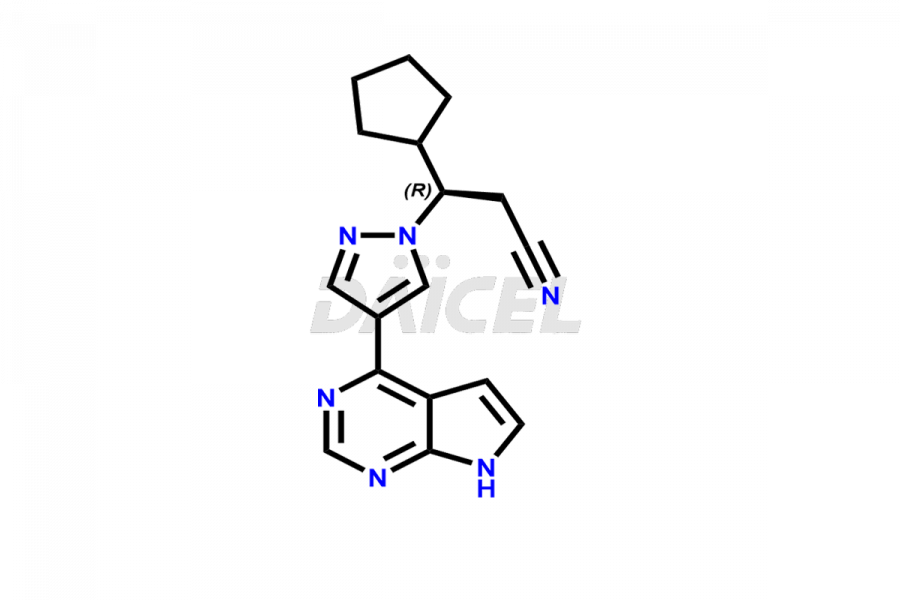
Ruxolitinib [CAS: 941678-49-5] is a drug used to treat intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis. It inhibits Janus-associated kinase (JAK) enzymes and has potential antineoplastic and immunomodulating effects. It is available as a phosphate salt.
Ruxolitinib: Use and Commercial Availability
Ruxolitinib is a medicine that belongs to the class of drugs known as Janus-activated kinase inhibitors (JAK). It selectively inhibits the JAK1 and JAK2 protein kinases. Ruxolitinib is FDA-approved for treating high-risk myelofibrosis, polycythemia vera patients intolerant or resistant to hydroxyurea, and steroid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. It is available in different tablet strengths under the brand name JAKAFI and as a topical cream under the name OPZELURA. In 2021, the FDA approved a Ruxolitinib cream formulation for mild to moderate atopic dermatitis, making it the first topical JAK inhibitor approved for use in the US market.
Ruxolitinib Structure and Mechanism of Action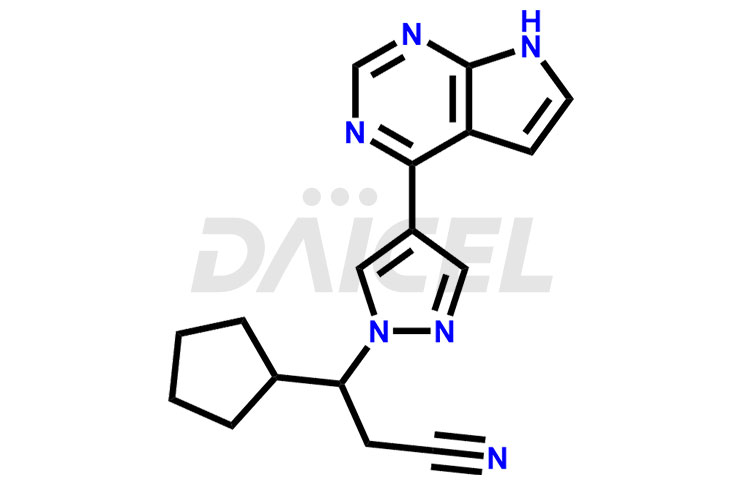
Its chemical name is (R)-3-[4-(7H-Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]-3-cyclopentylpropanenitrile. The chemical formula for Ruxolitinib is C17H18N6, and its molecular weight is approximately 306.4 g/mol.
Ruxolitinib belongs to the JAK inhibitor class of drugs that inhibit the protein kinases JAK1 and JAK2. The drug affects the signaling of several cytokines and growth factors responsible for hematopoiesis and immune function.
Ruxolitinib Impurities and Synthesis
During the synthesis1 of Ruxolitinib, several impurities may form, including diastereomers, regioisomers, epimers, and degradants. These impurities should be closely monitored and controlled during the synthesis of Ruxolitinib to ensure the safety and efficacy of the drug.
Daicel offers a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) from a cGMP-compliant analytical facility for more than twelve Ruxolitinib impurity standards, including Ruxolitinib R-isomer, Ruxolitinib M18 Metabolite, Ruxolitinib Triphenylphosphine oxide, Ruxolitinib Acrylopyrimidine impurity, etc. The CoA includes complete characterization data, such as 1H NMR, 13C NMR, IR, MASS2, and HPLC purity. We also provide 13C-DEPT and CHN on request. We also give a complete characterization report on delivery.
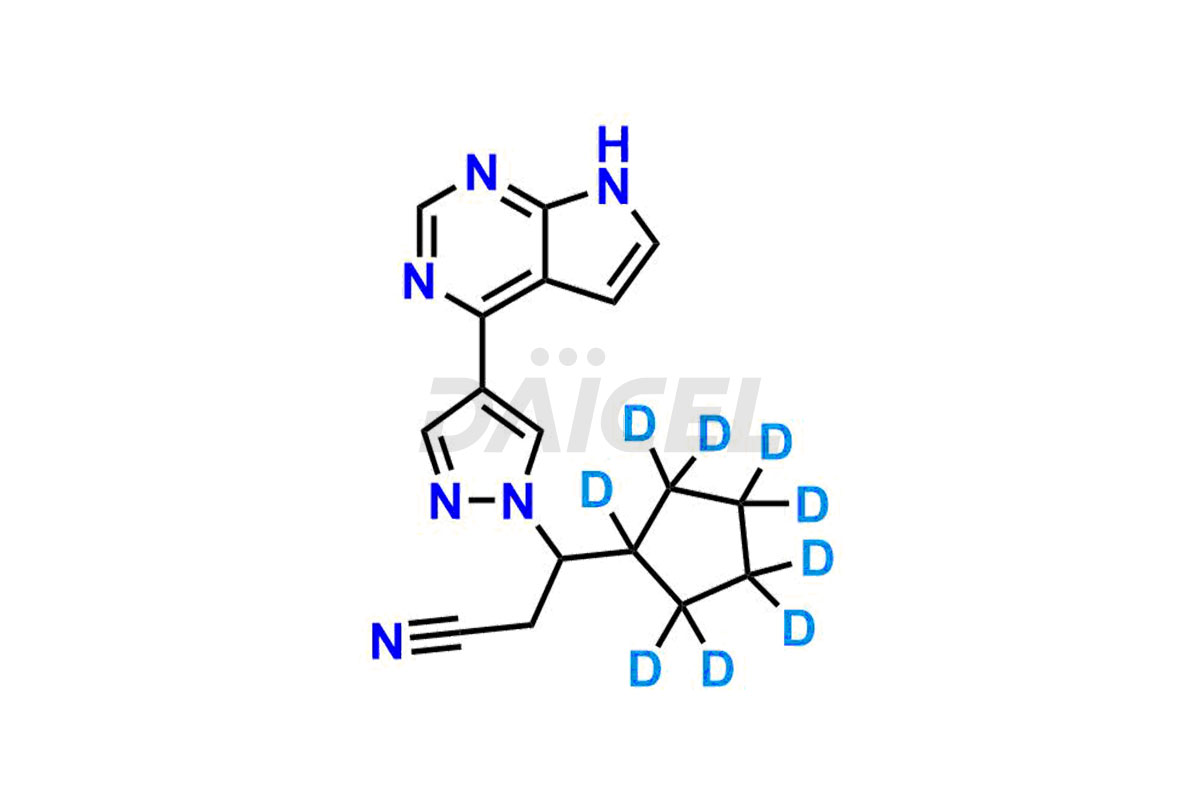
Daicel has the technology and expertise to prepare any unknown Ruxolitinib impurity or degradation product. The company also provides labeled compounds to quantify the efficacy of generic Ruxolitinib. Daicel offers highly pure isotope-labeled standards of Ruxolitinib for bioanalytical research and BA/BE studies. Daicel provides isotopic purity of labeled compound, Ruxolitinib-D9, in the CoA.